Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
i. Define and explain the concept of electronic configuration and its significance in understanding the arrangement of electrons in atoms.
ii. Describe the Aufbau principle, the order in which electrons fill atomic orbitals, and apply it to determine electron configurations of elements.
iii. Illustrate the electron configuration of different isotopes using their mass number and atomic number.
iv. Differentiate between electron configuration and orbital diagrams, recognizing the limitations of orbital diagrams.
v. Recognize the importance of electron configurations in determining chemical properties and bonding behavior of elements.
Introduction
The atom, the fundamental building block of matter, harbors an intricate world of electrons, negatively charged particles that occupy regions around the nucleus. Understanding how these electrons are arranged, known as electronic configuration, is crucial for comprehending the chemical properties and behavior of elements.
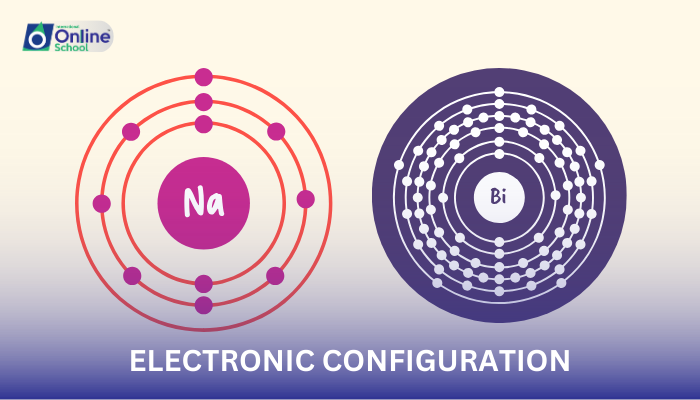
i. Electronic Configuration: A Blueprint of Electron Arrangement
Electronic configuration represents the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals, the specific energy levels where electrons reside. It provides a blueprint for understanding how electrons are organized within an atom.
ii. Aufbau Principle: Guiding Electrons to Their Orbits
The Aufbau principle, a fundamental concept in atomic structure, dictates the order in which electrons fill atomic orbitals. According to this principle, electrons fill orbitals of lower energy before moving to higher energy levels.
The Aufbau principle follows a specific sequence: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, and so on.
iii. Determining Electron Configurations
To determine the electron configuration of an element, we follow these steps:
- Identify the atomic number, representing the number of protons and electrons in the atom.
- Start filling electrons from the lowest energy level (1s), adding one electron per orbital until the level is complete (2 electrons).
- Proceed to the next energy level (2s) and continue filling orbitals until all electrons are accounted for.
iv. Isotopes: Diversity in Electron Configurations
Isotopes of the same element share the same number of electrons but have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in varying mass numbers. Their electron configurations remain the same, reflecting their identical atomic number.
v. Electron Configuration vs. Orbital Diagrams
While electron configuration provides the overall distribution of electrons, orbital diagrams represent the arrangement of electrons in specific orbitals. Orbital diagrams, though useful for visualization, have limitations, as they don't accurately depict electron movement or precise locations.
vi. Significance of Electron Configurations
Electron configurations play a crucial role in determining various aspects of an element's behavior:
Chemical Properties: Electron configurations influence the element's ability to form bonds and its reactivity.
Periodic Table Organization: Elements are arranged in the periodic table based on their electron configurations, reflecting similarities in properties.
Bonding Behavior: Electron configurations determine the number of valence electrons, which are involved in chemical bonding.
Electronic configurations, a fundamental aspect of atomic structure, provide a valuable insight into the arrangement of electrons in atoms. Understanding electron configurations is essential for comprehending the chemical properties, bonding behavior, and periodic trends of elements, laying the foundation for further exploration in the realm of chemistry.